ANDREA GRUNDT JOHNS
This text contains translated extracts from my master thesis written in March 2020. It is based on many years of research on photography, sight and perception. Have we lost the ability to see due to the enormous amount of visual material filling our daily lives? Are we being blinded by too much information? How can we, if need be, learn to see again? And what does seeing actually mean?
The original text was finished at the same time as large parts of the world were suddenly shut down, moved over to digital space, and thinking about touch became a pressing matter.
Le visible et l'invisible
I have walked 7,244,629 steps since I moved to Bergen 775 days ago. That is, approximately 9,348 steps per day. On a normal day, when I walk to the studio and back, I walk around 6,500 steps. Many governments now recommend an average of 10,000 steps per day. Several days this spring, my step count is down to only a few hundred steps a day.
___
There is an imbalance in our sensory system.
Vision separates us from the world, whereas the other senses unite us with it.
___
There are mirrors on the Moon to measure the distance between us and it. The mirrors were placed there during the voyages of Apollo 11, 14 and 15.
Light hits a surface, and a reflection is created. The surface's microscopic topography dictates all reflections. The surface catches the light and throws it back at us – either as the near perfect reflection in a mirror, or as the soft light on our living-room wall when the afternoon sun hits its rough surface. The smoother the microscopic topography, the more lifelike the reflection.
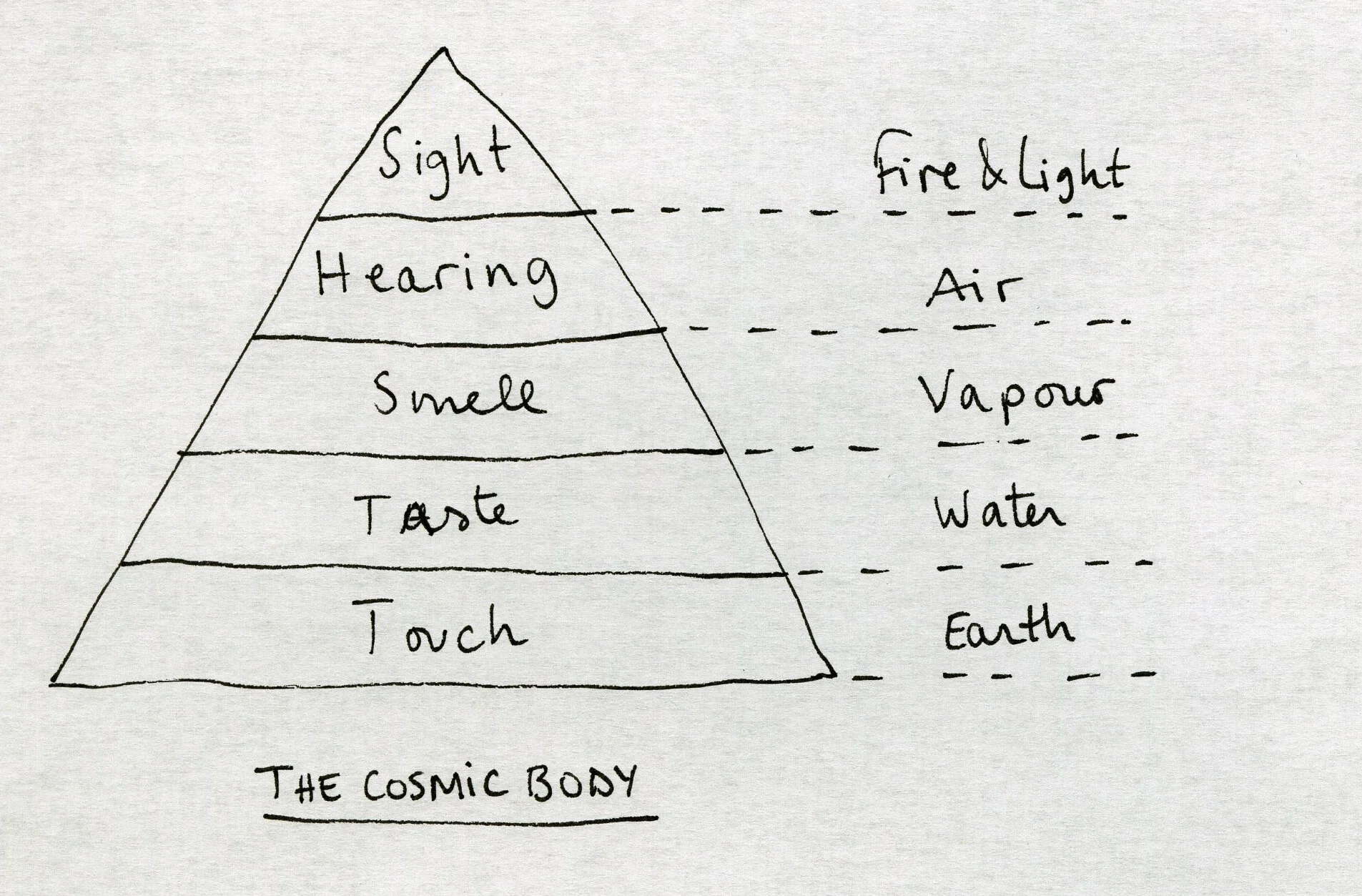
According to art historian Hans Belting, the ancient Greeks never really managed to decide if what they saw in the mirror was reality or trickery. This confusion is partly explained through their understanding of sight. Through the Emission Theory, Plato explains that we see because of light emitted from our eyes, that we see the objects in front of us only when the light from our eyes hits the object. The ancient Greeks’ idea of the Cosmic Body placed sight at the top of the sense hierarchy. Sight is light is fire is enlightenment. At the bottom is touch, and earth. Touch, treacherous, dangerous, confusing and seducing. Thus sight became the most important sense in the western world.
According to the Arab scientist Ibn Al-Haytham and his studies on optics from around 1,000 ad, there is an important difference between visibility, an optic phenomenon, and visuality, a psychological phenomenon. It is only through prefrontal mental synthesis that we are able to see, that we are able to understand and translate the light that hits our eyes. Memory and contemplation become essential in the process of seeing. Thus only details are needed to be able to understand the larger picture. We see because we have already seen.
A reflection is created when reflected upon.
Some months ago, I talked to a friend of mine who is currently working on developing eyes for robots. Their goal is to make robots that can see and recognise what is placed in front of them. A step closer to replacing humans with machines. The idea is fairly simple. The robot will get two ‘eyes’ – one working as a projector, emitting light, hitting the surfaces in front of it, the other as a camera recording and registering the shape of the object in front of it and the distance to it. They have already made great progress in their research.
___
We look, register and name. John Cage once said that we stop seeing when we start to name and categorise. ‘You look at a conifer [for instance] … and because it all looks basically alike [like other trees], you say it's a tree – and when you say that you cease to look. But only if you move from understanding to actual experience can you really begin to see.’ Seeing can lead to blindness.
___
There is something about being allowed to touch.
Last July in Japan I removed my shoes whenever I entered a space. Off with the shoes, on with slippers, or socks or barefoot. I feel an over thousand years old dark and smoothly polished wooden floor under my feet. It is burning hot in the sun, cooling, soothing in the shadows. After a long day in hard, dusty sandals, I step into the softest whitest plushest slippers and into a stark white art installation. Suddenly, I am inside the wooden floor, inside the installation. Suddenly I feel my surroundings. After a month of taking off my shoes I start to notice a certain change in perception, a certain change in the way I experience my surroundings. I have started to see with my feet. It occurs to me how much information I lose by wearing shoes. What if we wore gloves on our hands all the time?
Seeing with other senses can make us see again.
After thousands of thumbs being stuck into a hole in a column in Hagia Sofia in Istanbul and then twisted around 360 degrees for hundreds of years, the sweating-column, weeping-column, or wishing-column now has a clear scar on its side. The hole is as deep as a middle-sized thumb, and its contours are golden from the stroke of hands.
In a park in Oslo, the tightly clasped fist of a young bronze boy has become golden from the repeated touches from visitors. In the museum next door, the visually impaired could up until recently touch a few selected sculptures with signs in Braille.
At the Kiasma museum in Helsinki, all visitors are invited to press their hands against a cold, now dirty and greasy, marble plate at the entrance. Slowly we create a concave surface. Some time after my last visit to Kiasma, I read by chance in the foreword of The Eyes of the Skin by Juhani Pallasmaa, that the museum's name is a Finnish version of ‘chiasm’, a word the architect found in a chapter in Merleau-Ponty's Le Visible et l'invisible. The visible and the invisible.
There is something about being allowed to feel.
Some time before I move to Bergen I decide that I will walk wherever I go. Walking becomes my sole mode of transportation. I walk everywhere.
___
Our skin is our largest organ. Covering everything, making us feel with our whole body, the skin covers our tongue, our ears, our eyes. Touch is both external and internal. Touch is when we feel the humidity or the heat outside. Touch is when we feel pain or pleasure inside our bodies. Touch is when different body parts relate to each other without us thinking about it. Touch is the movement of our body. Touch is the only sense we cannot loose.
Lately, the word ‘haptic’ has emerged when talking about our sense of touch. The haptic refers to a combination of sight and touch, allowing us to understand and feel texture without touching. But to do this we have to touch first, to create a library of haptic memories.
Once, I experienced the lack of touch over a longer period. I had just moved away from home for the first time, and had almost no physical contact with others for half a year. It felt as if my body was imploding. Silently, slowly, sucking, sinking into itself. I was amazed and baffled. I remembered the horror stories from my childhood about orphanages where children grew up with serious disorders due to the lack of touch.
___
We break the surface. We see with our hands and feel with our eyes. They lead our fingers quickly over the touch-screens. We cannot feel our way anymore. How do you feel an app?